Setting up a pasta production line can be a complex and costly endeavor, but it offers lucrative returns in the thriving food industry. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key factors influencing the cost of establishing a pasta production facility. From initial investments in equipment and machinery to ongoing expenses such as raw materials and labor, we’ll explore the various components that contribute to the overall budget. Additionally, we’ll discuss factors like location, scale of production, and compliance with industry standards, helping you gain a clearer picture of what it takes to turn your pasta production dream into a reality. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or a budding food industry enthusiast, this guide will equip you with valuable insights to make informed financial decisions for your pasta production venture.
What Is Involved in Starting a Pasta Production Business?
Essential Raw Materials for Pasta Manufacturing
To commence the pasta manufacturing business, several key raw materials are required. The main ingredient is high-quality durum wheat semolina with vital protein and gluten contents needed to make tough but elastic pasta. Additionally, there is a need for water which is used in mixing or hydrating the semolina into dough. Depending on the type of pasta being made, other possible ingredients are; egg in egg pasta types, vegetable purees and powders as colorants/flavourings of pastas and specific additives like salt, preservatives etc. to enhance taste and shelf life. In addition, good packaging materials should be procured to ensure that the product remains fresh and preserved during movement and storage.
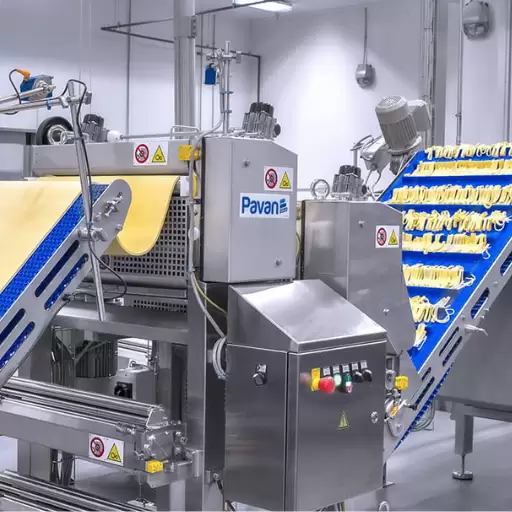
Machines Needed For Making Pasta
In order to start an effective operation of a pasta production factory, one needs machines which are summarized below:
- Mixing Machine: This machine combines durum wheat semolina and water making a consistent dough by thoroughly stirring together the ingredients until they achieve the desired texture and elasticity.
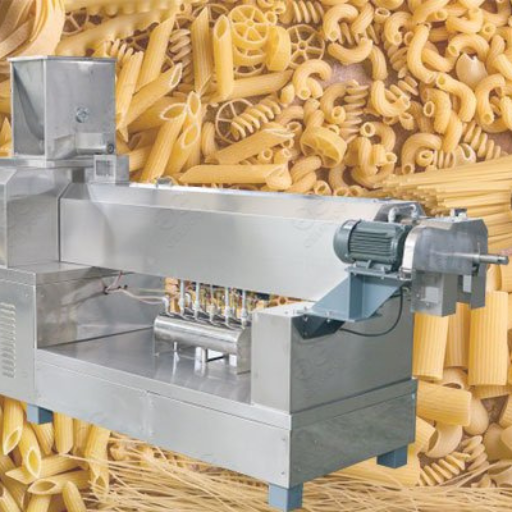
- Extruder: The extruder gives various shapes to the dough such as spaghetti macaroni penne etc., by pushing it through different molds or dies.
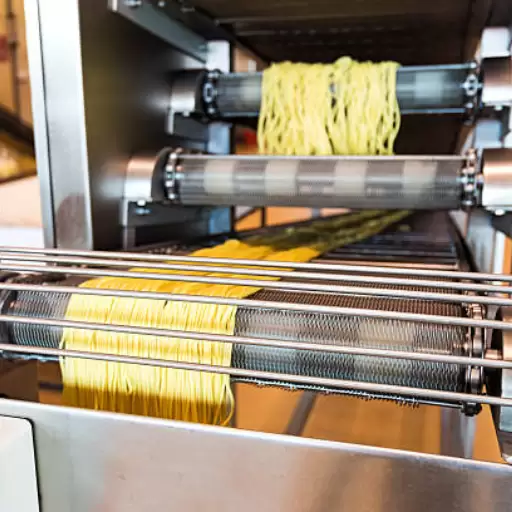
- Dryer: Appropriately drying the pastas helps in guaranteeing their life span. A dryer gradually removes moisture from fresh-made pastas so that it does not form molds on it and attains necessary hardness levels.
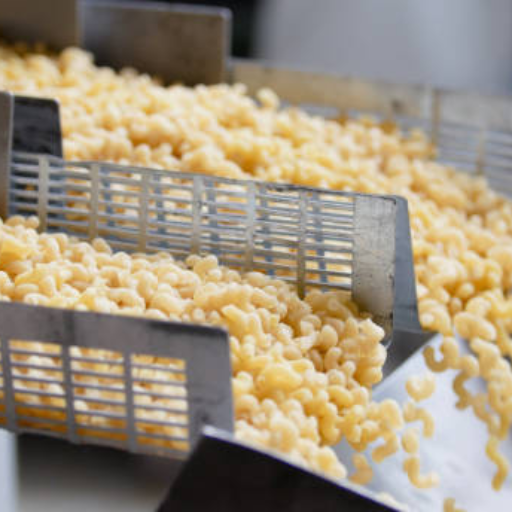
- Cutting Machine: At this point cutting machine comes in handy; it is used for cutting off the extruded pasta into reasonable lengths hence ensuring uniformity as well as precision with respect to length.
- Packaging Machine: Packaging machine ensures freshness as well as protection of pasta from contamination. With these machines you can easily seal up packages and have them ready for shipping so that they reach consumers without losing quality.
These equipments form part of essential machinery used in transforming raw materials into final marketable products ready for market consumption.
Understanding the Pasta Production Process
The process of pasta production has several important stages that must be followed for high quality end products. Here is a brief overview based on excerpts from some of the leading websites in this field:
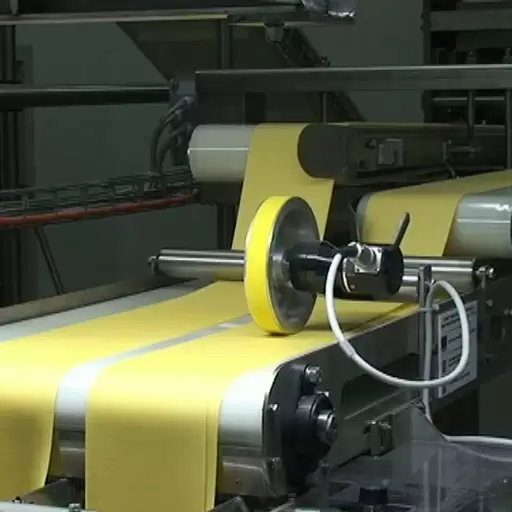
- Mixing: Start by combining high-quality durum wheat semolina with water. This step involves mixing to form dough, ensuring its consistency and moisture level throughout. Complete kneading of the mixture results in dough elasticity.
- Extrusion: Once the dough is prepared, it goes through an extruder. The latter forces the dough through moulds or dies which enable it to acquire various shapes such as spaghetti, fusilli and penne among others.
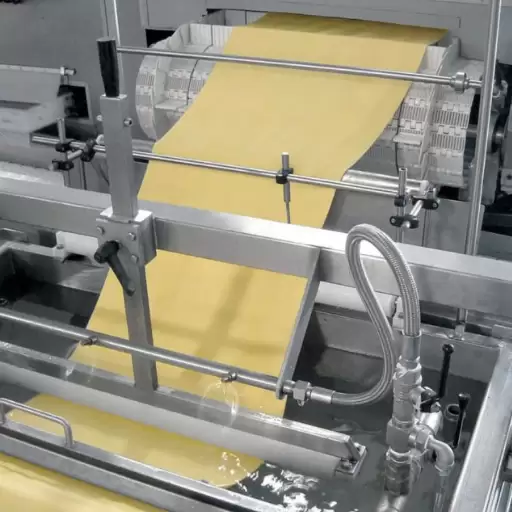
- Drying: Extruded fresh pasta is then transported to a dryng stage. It includes gradual withdrawal of moisture during controlled drying conditions at specific temperatures and humidity levels; otherwise, molds will develop hence spoiling it.
- Cutting: At the right point when it attains a desired degree of dryness, the product can then be cut into appropriate lengths. Cutting machines ensure uniformity and precision needed in packaging and further processing.
- Packaging: The last thing that happens before dried cut pasta gets shipped out are automated packaging machines which pack them up. Packaging helps preserve freshness while also protecting against dirt or other impurities present in air thus making them fit for distribution.
Each stage is necessary for producing market-oriented pasta with consistent taste levels as well as quality requirements.
How Much Does It Cost to Start Pasta Production?
Initial cost to set up production line
Starting a pasta production line involves several main expenses. According to the current top websites, the following are the initial costs divided into classes:
- Machinery and Equipment: A good investment in making machines which produce quality pasta is inevitable. Such machines can be worth anywhere from $100,000 to $500,000 depending on the make, capacity and automation level.
- Factory Space and Utilities: Renting or buying suitable space that conforms to health and safety standards is another big expenditure. This may include paying for premises plus putting in place basic utilities like water, power and air conditioning whose charges can range between $50,000 up to $200,000.
- Raw Materials: Provision should be made for the first purchases of raw materials such as durum wheat semolina as well as packaging supplies. The initial cost of raw materials usually amounts to around $10,000 – $50,000 depending on the scale of production.
- Labour: Employment of skilled labour for machine operation, quality control and packaging is central. Initial costs of labour (inclusive of training) come at different prices but can begin at about $20 000 till around$100 000.
- Compliance & Licensing: To comply with public health & safety guidelines as well as obtain necessary permits/licenses will require financial input ranging between $5000-$20000.
On average therefore it costs anything between approximately $185 000 and about $870 000 to start up a pasta product line with factors like production capacity, equipment’s quality or location influencing this amount.
Ongoing Costs Associated With Production
- Raw Materials: This is an ongoing expense due to purchasing high-quality raw materials such as durum wheat semolina every time it runs out. Depending on output levels and market rates per month spending may vary between approximately $10k-$50K.
- Labor: Salaries paid regularly to workers manning operations plants, ensuring standards are maintained through inspections and employees in the human resources department are examples of such expenditures. Depending on the number of employees and wage rates, a month’s wage bill can begin at $5,000 up to $30,000.
- Utilities: In order to continue being in production, these include electricity, water, gas and waste management fees that have to be paid for. Normally this ranges from about $2 000 -$10 000 per month due to varying levels of output or efficiency of equipment.
- Maintenance and Repairs: To keep machines working well during production it is important to do regular servicing as well as any required fixing. These costs may vary greatly but usually build up around $1000-5000 every month.
- Marketing and Distribution: Sales promotion activities as well as means through which goods reach the consumers remain essential hence incurs some expenses. These figures may be anything between $2000 – $15 000 monthly depending on scale and market penetration.
In conclusion therefore, ongoing expenditure regarding maintenance of pasta production line is critical for operations sustainability ranging from about $20k-$110k per month for different factors like volume of production, labor costs among others.
Estimated Cost Per Unit Of Pasta
Several factors must be taken into account when estimating cost per unit of pasta. Based on current industry data:
- Raw Materials: The key component, durum wheat semolina, normally costs between $0.30 and $0.50 per pound. Taking into account water and packaging materials also included in making one pound of pasta raw materials should range from $0.35 – 0.55 depending on company’s price policy.
- Labor: Labor overheads cover wages paid to those working on the machine assembly line performing quality checks or carrying out office assignments . The cost incurred by an employer in paying his workforce per pound is projected as being around$0.15-$0.25 only considering other aspects known to affect pricing .
- Utilities, and maintenance: Utility bills such as electricity, water and gas, plus repairs and maintenance, make up about $0.05 to $0.10 per pound of pasta.
- Marketing and Distribution: The cost is estimated at $0.10 to $0.20 per pound for its advertising and distribution.
Adding the above elements together the total estimated cost per pound of pasta could be anywhere between $0.65 to $1.10; these figures may differ based on production volumes, efficiency levels or market conditions in place.
What Are the Different Types of Pasta Produced?
Production costs of popular pasta shapes
There are many different pasta shapes, each having its own set of production costs due to differences in machinery setup, production time and raw material requirements. According to the most common sources, following are some frequently manufactured and consumed types of pasta:
- Spaghetti: A common choice for many homes, spaghetti is one of the simplest pasta shapes to produce. Its simple cylindrical shape requires lesser complex machines as well as takes lesser time for manufacture. This leads to lower cost of production that usually ranges between $0.55 and $0.75 per pound.
- Penne: Penne pasta is popular because it can be used in various recipes such as salads. It is tubular with diagonal cut ends. The manufacturing process for penne employs more complex machinery than spaghetti does hence slightly increasing the cost of producing it. In fact, this type of pasta may cost from around $0.70 per pound to roughly $0.90 per pound.
- Fusilli: Fusilli has a spiral shape that needs extrusion machines with spiral parts specifically designed for making it leading to increased complexity and time taken in processing it thus raising its unit costs. As such, the average cost of producing fusilli is higher ranging generally from about $0.80 up to around $1 per pound.
These estimated costs may change depending on efficiency levels at the plant, scale effects or prevailing market forces necessitating continuous reviews by producers over production processes and their associated costs.
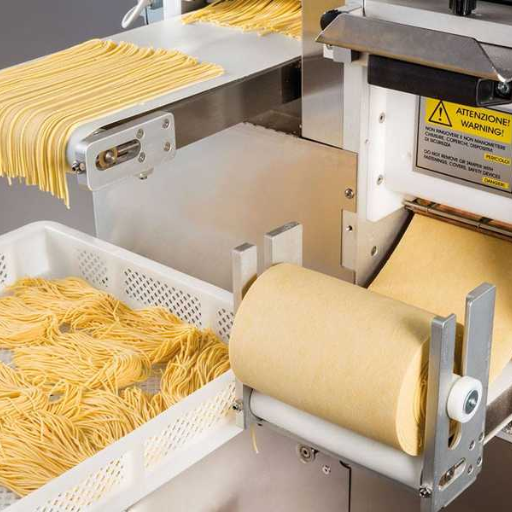
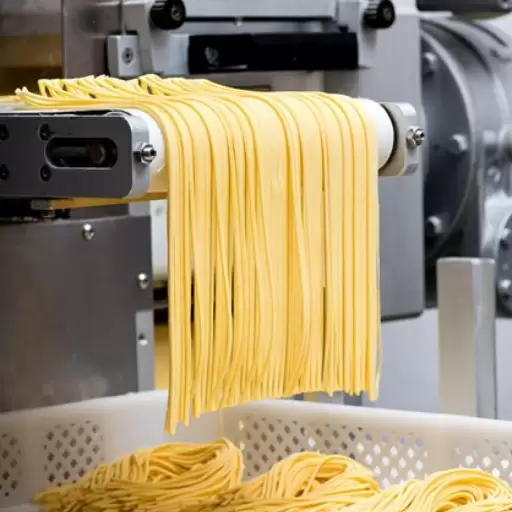
Production Methods for Fresh Pasta vs Dry Pasta
The techniques employed when making fresh pasta differ immensely from that approach used when queuing dry pastas with distinct methods applied in both cases.
- Fresh Pasta: Freshly made pasta simply consists mainly flour and eggs (or water) mixed into a dough form which after mixing together then kneading until suitable consistency is achieved; the dough shall have arrived at the right point. The dough can either be rolled out by hand or through a pasta machine to attain the appropriate thickness. The rolled dough may therefore be cut into various shapes, sizes, Fresh pasta is usually cooked immediately or refrigerated for short-term storage. It is soft in nature and to maintain it in that state fresh pasta should be handled delicately thereby preferred for dishes high on delicate flavors and textures.
- Dry Pasta: On the other hand, dry pasta has an industrial scale of production with its dough mainly composed of semolina flour and water. Paste made using this recipe will be mixed and kneaded using industrial mixers before being extruded through dies that give them their specific shapes. The most important difference occurs during drying; once formed, the pasta goes through controlled drying at low temperatures across long periods of time. This form of dehydration ensures that it can have a long lasting shelf life as well as remain intact throughout transportation and storage. As the moisture is not only eliminated but also texture altered by drying process so that when cooked dry pastas are firmer which makes them suitable for many kinds of heavy sauces.
Both methods offer different culinary experiences whereby fresh pasta gives a tender and richer mouth feel while dry pasta offers strength with a tough texture best suited for manifold solid dishes.
Pasta Market Demands Trends
Several key factors are reshaping consumers’ preferences and industry practices in the current trend of pasta market demands.
- Health and Wellness: Consumers who are watchful about their health prefer pasta that fits into their dietary goals. These include gluten-free pasta, whole grains varieties, and more fortified pasta with other nutrients like protein and fiber. Also, rising is the inclination for organics as well as GMO free pastas as consumers grow more aware of ingredients they use.
- Sustainability and Ethical Consumption: Environmental concerns dictate the demand for its sustainably sourced and ethically produced pasta products. Eco-friendly packaging has come to be a focus now for many businesses whilst at the same time sourcing ingredients from sustainable farms. Transparency in this supply chain is a major selling point brand positioning for companies that target environmentally conscious customers.
- Convenience and Innovation:Busy lifestyles are driving demand for convenient / easy to prepare pasta products. Ready-to-eat past meals innovations such as those that can be cooked within seconds or minute’s microwavable options have become increasingly popular in recent years. Such types cater to time-starved customers who still desire tasty yet healthy dishes without wasting much time during preparation process.
By being aware of these emerging trends, firms within the spaghetti sector will be better positioned to satisfy consumers’ needs as well as stay competitive in a changing market environment.
What Equipments Are Required for Dry Pasta Production?
Functions of a Pasta Extruder
A pasta extruder is one of the most important machines in the production of dry pasta and helps in achieving quality and uniformity. Firstly, it is through the machine that dough is thoroughly mixed or kneaded to ensure proper blending of its ingredients all over. The texture and elasticity desired for the pasta are dependent on this stage.
The paste is shaped by forcing it through various molds or dies. It is these dies which determine how thick or thin the final pasta will be thereby allowing for different shapes such as spaghetti, penne among others. Accurate shaping ensures every piece cooks evenly.
Additionally, drying takes place with its help once extrusion takes place. As soon as extruded from the equipment, they are partially dried either by exposure to air or heat under controlled conditions. This early drying phase gives shape and form to these pastas after which they go through a final drying process that assures them safe moisture levels for storage purposes.
In general, a pasta extruder simplifies manufacturing operations making it possible to produce an assortment of quality pastas.
Role of Pasta Dryer in Pasta Production
A pasta dryer plays a critical role in ensuring that there is low moisture content on extruded pasta for long life span as well as prevent microbial growth during storage thus making it durable dry pasta. Normally, this drying procedure involves several careful steps where different temperatures and moistures are regulated within each step until last one without which even cracking may develop or brittleness may occur because gradual approach holds up the structure and texture of these food substances.
Commercially available dryers can handle large quantities at once due to their massive sizes with advanced technologies used to control variables throughout industrial drying process. Usually such machines have more than one chamber containing the products being dried while some automatic systems enhance consistent outcomes can also be applied here because appropriate desiccation guarantees firmness needed when eaten or cooked al dente apart from shape maintenance and retaining nutritive value as well.
The pasta dryer is a must-have in the manufacturing process because it ensures that the product is marketable, safe and of high quality.
Benefits of Using High-Quality Machinery
Using top-notch machines in pasta production has several advantages that improve both efficiency and quality of final products. First, machines of high caliber are made with accurate engineering and robust materials, hence improving their durability while lowering maintenance cost and minimizing downtime. Secondly, modern machinery comes with the latest technology that enables precise control over various production parameters resulting in uniformity throughout. Such high automation levels help to curb human errors at work while boosting output during mass industrial processing without sacrificing its superiority. Moreover, such top-quality devices often contain special attributes improving sanitation as well as facilitating easy clean up necessary for maintaining proper hygiene. These machines save energy as they operate thus are cost-effective besides being environmentally friendly too. In brief, procuring excellent machinery guarantees better product quality, efficient operations and longer term financial gains for an organization.
How to Maximize Production Capacity in a Pasta Factory?
Making Production Lines Efficient
To optimize efficiency in production lines of a pasta factory, I begin by assessing and reorganizing the workflow with a view to eliminating any possible bottlenecks and unnecessary steps. I streamline processes by adopting advanced automation and robotics where applicable thereby resulting in an increase in productivity through fewer errors. Additionally, regular maintenance is required as well as timely machine upgrades to guarantee peak performance and prevent breakdowns. This helps me fine-tune operations continuously since real-time monitoring systems are priceless as they provide data-based insights on it. Furthermore, I train my staff constantly so that they can be able to keep up with the latest technologies/ trends.
Pasta Products with Consistent Quality
Poor quality control begins with poor quality sourcing of key raw materials such as high-quality durum wheat semolina. I have strict supervision over the production process which is characterized by standardized recipes and accurate measurements so that there can be uniformity in flavor and texture. By carrying out rigorous quality control checks at each phase starting from mixing & extrusion right through drying & packaging all defects come up immediately for rectification. We ensure that all our machinery are calibrated regularly and we do frequent quality audits as we cannot compromise on the final product. In addition, I keep myself updated about any new developments within my industry so that I can enhance consistency and quality of our pasta products using innovative techniques.
Scaling Up Production: Macaroni to Spaghetti
Scaling up from macaroni to spaghetti presents several critical steps for a smooth transition while ensuring product quality standards are maintained at all cost. First of all, I evaluate our existing manufacturing capacity identifying any constraints that might impede scaling up the production levels. It becomes necessary to upgrade or add new machines specifically designed for spaghetti making because its shape and drying requirements differ from those of macaroni significantly. Key points towards optimizing our production line for efficiency include dough mixing through to final drying stage/processes being undertaken. On top of machinery enhancements, our personnel are also trained to handle specificities that come with spaghetti production. This ensures quick monitoring of performance in real-time, while making prompt necessary changes accordingly through the implementation of advanced systems. As I systematically address each phase, I effectively streamline our operations in order to scale up spaghetti production while still maintaining high standards expected by our customers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Mention the key expenses of setting up a dry pasta manufacturing facility
A: The main costs include the price of buying pasta production lines, obtaining industrial pasta machinery like a pasta maker, cutter and packing equipment, and also raw materials costs including wheat flour. Another cost is for factory space, labor and shipping.
Q: What are the main ingredients used in pasta making?
A: Mainly materials employed in making pasta commonly consist of wheat flour, water and sometimes eggs. These components are essential to come up with different kinds of pastas ranging from ravioli through fusilli to dry macaroni.
Q: How do different factors affect cost when establishing a pasta production site?
A: Among factors that influence overall cost of starting a pasta mine include scale of production, choice on type or variants of Pasta Production Lines chosen by buyers or consumers as well as labour charges. This is vital knowledge for decision makers.
Q: How much does equipment for a pasta production line typically cost?
A: The variation in prices is really high. A fully equipped dry type will vary between fifty thousand dollars to five hundred thousand dollars or more depending on company’s output capacity and requirements; which includes high-quality machinery such as cutters and makers.
Q: What are the shipping costs associated with importing pasta production equipment?
A: Shipping charges paid when bringing these machines into your country may differ according to weight and size of machine as well as distance it is transported over & mode used. You should consider all this while planning your financial plan.
Q: How do I decide between long-cut pasta and short-cut pasta production lines?
A: It all depends on what areas you want to concentrate in producing for instance markets demand. For long cuts like spaghetti different settings have to be made regarding equipments such as penne Or macaroni whereas short- cut options need other considerations. Look at your targets market assessment together with what you intend to produce so as to determine which type should be processed.