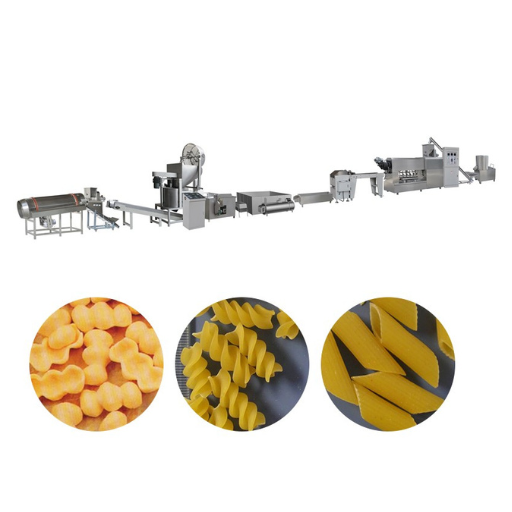
Macaroni, a beloved staple in countless cuisines worldwide, has a fascinating journey from wheat field to dining table. This blog aims to unravel the intricate process behind macaroni production, shedding light on each step from the initial harvesting of wheat to the final packaging of this versatile pasta. We will explore the transformation of raw materials, the machinery involved, and the quality controls that ensure consistency and taste. By the end of this comprehensive overview, readers will gain a deeper appreciation for the macaroni they enjoy and the meticulous process that brings it to their plates.
Understanding the Macaroni Manufacturing Process
From durum wheat to dough: The process of transformation
Macaroni starts its journey from durum wheat, this is a hard type of wheat with high protein and gluten. This makes it the ideal raw material for pasta making. These are some of the stages that durum wheat goes through:
- Cleaning and Conditioning: The wheat grains first have to be cleaned by sieving off impurities which may include stones, dust and other foreign materials. Different sieves, air classifiers and aspirators are used during this cleaning process.
- Conditioning takes place right after cleaning: Where water is added in specific amounts so as to maintain moisture content at about 15-17% such that when milled, it will produce flour with desired quality characteristics.
- Milling: After conditioning the wheat can now be milled through several rollers that change into semolina or stiffened flour that contains much protein. Bran and germ are separated from the endosperm by grinding operation followed by different types of sifting until a uniform size between 180-300 microns.
- Mixing and Kneading: Then water is added to semolina so as to form a dough which usually has about 30-32% water content enough for consistency desired. High rate mixers are used while mixing so as to ensure equal hydration takes place in all parts leading to development of gluten networks responsible for attractive pasta elasticity.
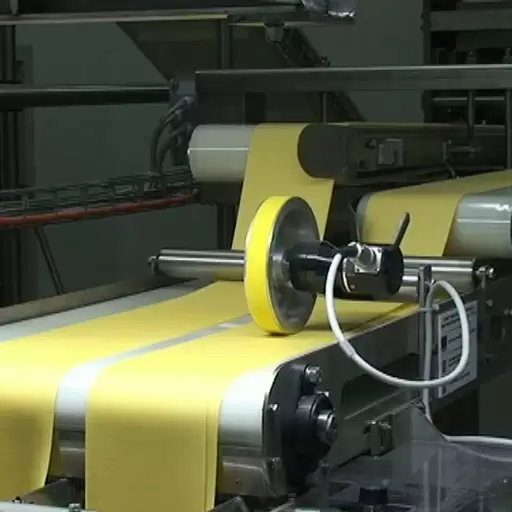
- Extrusion: Dough made from the above mixture is conveyed into extruders fitted with macaroni dies. Under moderate heat (40-50°C) and high pressure (10-15MPa) operation conditions, these dies force out dough thus creating macaroni shapes having uniformity.
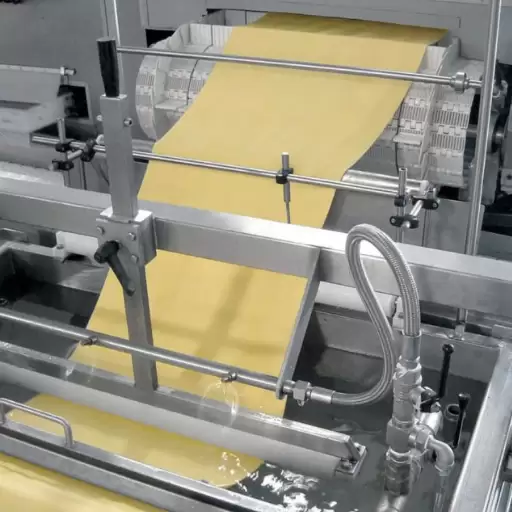
- Drying: Just after emerging from the die, macaroni is dried in numerous steps whereby moisture content reduces gradually from around 30% to below 12%. Drying occurs at two distinct temperatures namely pre-drying (50 – 60°C) and final drying (70 – 90°C). This is aimed at preserving the shape of macaroni when cooking as well as preventing cracks.
- Cooling and Packaging: The cooked macaroni is then cooled to about room temperature in order for it to be stable. It is then sealed appropriately using moisture proof bags that will keep it fresh and away from bacteria.
The above steps, characterized by exact technical parameters and rigid quality control guidelines change raw durum wheat into the end product which is consumed globally. By understanding this meticulous process, one can truly appreciate the artistry and science behind crafting macaroni.
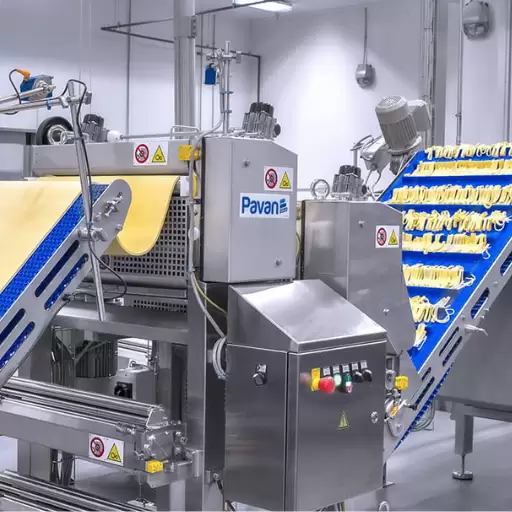
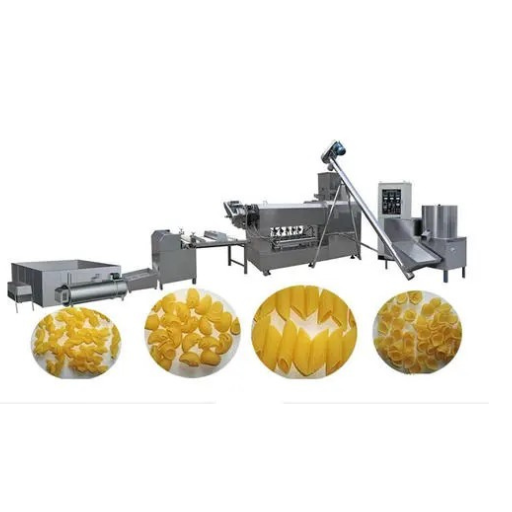
Extrusion process shapes macaroni
Extrusion method plays a significant role in shaping macaroni by converting semolina dough into uniform pasta shapes through applying high pressure together with moderate temperature. The dough goes through special dies that are designed to give specific size and shape of the macaroni. In result, it brings out uniformity, grainy sensation on touch as well as strength hence familiar appearance of a cylinder like form of macaroni.
Drying plays an important role in producing macaronis
Macaroni making involves a drying step which is crucial in determining the texture, hardness and shelf life of the pasta. The moisture content is gradually reduced from 30% to less than 12% to avoid cracking and maintain the shape of the pasta. This controlled drying process, consisting of pre-drying steps followed by final drying at precise temperatures and humidity levels is needed to stabilize macaroni’s structure as well as preserve its quality. Correctly dried pasta provides storage durability and transportability while cooking normally without altering its intended texture.
The Essential Machinery in Macaroni Production
Choosing the right extruder for perfect macaroni shapes
There are many factors to consider when selecting the most suitable extruder for macaroni production, which will help in achieving pasta shapes of uniformity and high quality. Here is what you should look out for:
- Pressure and Temperature Control: The main thing is that the extruder must be capable of maintaining a stable high pressure and moderate temperature. This consistency ensures that the dough is adequately compacted and gelatinized, giving it a smooth texture. Typical pressures range from 50-100 bars while temperatures are maintained at about 40-50°C.
- Die Design and Material: These components should be made of Teflon or bronze, which are strong enough to withstand any corrosive food effects. Their designs determine how these paparazzi shaped pastas would appear like and this would require precision engineering to make them so.
- Throughput Capacity: For large-scale operations, an extruder should have an appropriate throughput capacity. Throughput capacities ranging between 100-200 kg/hour are common in small-to medium scale outfits whereas capacities can exceed 500 kg/hour in large industrial units.
- Automation and Control Systems: Modern extruders come with automated control systems that monitor pressure, temperature, as well as dough consistency thereby greatly enhancing productivity and product consistency. Such systems should possess real-time data feedbacks as well as adjustment capabilities.
- Power Consumption: Efficiency of energy use is paramount. An efficient power usage ranges from about 20-50 kW for medium scale plant size; hence can significantly lower operating expenses incurred.
Observing these parameters will allow selecting an extruder that produces consistently ideal macaroni shapes thus contributing towards both quality enhancement and improved production efficiency.
Drying Equipment: Ensuring the Ideal Texture and Shelf-Life
The best selection of drying equipment leads to obtaining the desired texture as well as shelf-life for macaroni. Drying removes moisture from pasta hence it is a critical step in preventing microbial growth and spoilage. Here are key considerations for drying equipment:
- Types of Dryers: Commonly used dryers include static, belt, and continuous dryers. Each type offers specific advantages; for instance, static dryers provide uniform drying, while belt and continuous dryers are more suitable for high-volume production lines.
- Temperature and Humidity Control: What matters most here is that temperature control as well as humidity should be precise. The best drying occurs at 60-90°C with carefully controlled humidity to avoid over-drying or under-drying which can affect texture and durability.
- Drying Stages: Generally pasta drying includes pre-drying, main drying and final drying stages. At each step different temperatures and humidities should be set to progressively reduce moisture contents without compromising the structure of the pasta.
- Airflow Dynamics: Proper airflow ensures even drying and energy efficiency. Advanced drying systems utilize sensors to monitor and adjust airflow, ensuring consistent results.
- Energy Efficiency: The air travel process must conform to energy saving strategies so as to enable customers cut on their day-to-day operational expenses. For example, modern dryers have heat recovery systems.
By investing in state-of-the-art drying equipment that offers precise control and efficient energy use , producers can ensure macaroni that boasts an ideal texture, extended shelf-life, and superior quality.
Packaging Solutions for Macaroni Products
For macaroni products effective packaging solutions play a crucial role in preserving product quality thus extending product shelf life thereby satisfying the consumers’ requirements fully. Consider three key factors below:
- Materials: The choice of packaging material is critical. Common types are paperboard, plastics and composite materials. Plastic wrappers like polyethylene and polypropylene have excellent water resistance that ensures the pasta remains fresh and dry. Paperboards may be an environmentally friendly option, often used with a plastic liner for better protection.
- Durability and Barrier Properties: Good packaging should guard against physical damage, light, as well as oxygen all of which degrade the pasta. High barrier materials such as multilayered plastics can effectively prevent moisture and air from reaching it thus maintaining its color, texture and taste. Rigid structures such as corrugated boxes may also provide an additional level of robustness in order to protect against any impact that may occur during transportation.
- Sustainability: Sustainable packaging has become crucial in light of growing environment concerns. There is now increasing demand for degradable or recyclable packages. For instance, innovations involving compostable films made from plant-based polymers help in reducing environmental footprints. Eco-friendly packaging not only appeals to eco-conscious consumers but may also be aligned with corporate sustainability goals thereby enhancing brand image.
By giving attention to these aspects producers can select packing alternatives that will secure macaroni products besides taking into account modern consumer expectations and sustainability trends.
Exploring the Spaghetti vs. Macaroni Production Techniques
Comparing the manufacturing processes
Spaghetti Production:
- Mixing and Kneading: The process starts with mixing durum wheat semolina/flour and water. The dough is then kneaded until it reaches the desired consistency, which typically takes around 20 minutes. Technical parameters are either; water content (30-32%), kneading time (20-30 minutes), and dough temperature (50-60°C).
- Extrusion: The spaghetti die forces the dough through it, giving spaghetti its long, thin strands. Technical parameters include; extrusion pressure (70-110 bar), die temperature (40-50°C), and extrusion speed (2-3 m/min).
- Drying: Freshly made spaghetti gets dried indoor in a controlled environment to reduce moisture content to about 12-13% for good texture and shelf life. Some technical parameters here are drying temperature (60-80°C), drying time (8-12 hours) and humidity control (55-65%).
- Packaging: Finally, dried pasta is cut into required lengths, cooled if necessary, and packed using moisture resistant materials to keep them fresh.
Macaroni Production:
- Mixing and Kneading: Like spaghetti production macaroni production begins by mixing durum wheat semolina/flour with water. However, the dough has to be kneaded to an appropriate consistency but this might slightly differ due to different shape requirements of each type of pasta. Technical parameters are either; water content (30-32%), kneading time (20-30 minutes), or dough temperature (50–60°C).
- Extrusion: Here, macaroni dough is passed through macaroni dies that make short hollow tubes. Some of technical parameters are; extrusion pressure(90 -120 bars), die temperature(40 – 50 °C)and extrusion speed(1 5 – 2 5 m/min).
- Drying: Moisture content is reduced to about 12-13% by drying the extruded macaroni in controlled conditions. Some technical parameters here are drying temperature (60-80°C), drying time (8-12 hours) and humidity control (55-65%).
- Packaging: Dried macaroni is cooled before being packed in moisture-proof packages.
By analyzing specific technical parameters and processes involved, it is evident that both spaghetti and macaroni production have some common steps but major differences exist between the two products during the extrusion phase due to different shapes and respective technical requirements.
How Different Raw Materials Influence the Final Product
The choice of raw materials significantly affects quality and properties of pasta such as spaghetti and macaroni. Thus, use of different types of flour or semolina, water quality, even optional ingredients can substantially change the texture, taste, nutritional profile of the product.
- Flour Quality: Durum wheat semolina contains high gluten proteins making it ideal for pasta with a firm texture that holds shape well. Using alternatives like whole wheat flour, chickpea flour or rice flour can change taste, texture and nutritional composition. Whole wheat adds more fibre and nuttier flavour while rice flour produces a soft textured gluten-free product.
- Water Quality: Water quality used in dough mixture may be overlooked but it has an impact in final products. Water minerals can influence gluten development which affects pasta elasticity and texture. Use purified water to eliminate unwanted minerals that interfere with dough consistency.
- Additional Ingredients: The addition of eggs, spinach or tomatoes among other things would boost the flavor, color; protein content , vitamins etc., for example egg makes for richer pastas with smoother texture while vegetable based ones may provide more nutrients along with different shades on them.
In making a choice and striking a balance within these constituents pasta makers can make products that cater for set tastes, dietary needs, as well as quality considerations specified by the market.
Why do Spaghetti and Macaroni get defined by the extrusion shapes?
Extrusion shapes are essential in determining spaghetti and macaroni. They decide its texture, cooking time, and how well it holds sauces. Spaghetti is made by pushing dough through a circular die to produce thin long strands. This shape is ideal for smooth oil based sauces like aglio e olio or light tomato sauces because it allows the sauce to coat the strands evenly without overpowering them.
On the other hand, macaroni is made by pushing dough through a die with a hollow center, creating short tubular shapes. The hollow middle is good for this design as it traps sauce ensuring you have full flavored bites. Moreover, ridges commonly found on different types of macaroni help hold more sauce hence improving overall eating experience. Therefore, shaping forms in extrusion are necessary to achieve required culinary outcome in each type of pasta.
The Importance of Selecting High-Quality Raw Materials
Why semolina and durum wheat are the gold standards
Pasta manufacturers consider durum wheat and its byproduct, semolina, as gold standard because of their distinctive properties. Durum wheat contains high amount of protein and a strong gluten network which are important in making firm, elastic dough that keeps its shape when cooked. Semolina, a coarse ground flour from durum wheat, has a grainy texture, nutty flavor that allows the sauces stick onto pasta . Moreover, the high yellow pigment present in durum wheat imparts to pasta an appealing golden color. In this way, pasta produced from semolina and durum wheat is unmatched both in taste and texture hence presenting a premium option for themakers of pasta or consumers.
The impact of water quality on macaroni production
Water quality significantly affects macaroni production with regard to consistency of the dough and quality of the final product. High-quality water that is low in mineral content but free from contaminants is crucial in order to achieve desired texture as well as elasticity of dough. On the other hand hard water with lots of calcium and magnesium may lead to tougher dough resulting poor cooking quality of pasta. Similarly if it is very soft or acidified it can also affect gluten network within the dough making it weak. Thus optimal water quality will help maintain shape and texture during cooking for macaroni hence obtaining a good end product.
Exploring alternative raw materials for niche markets
Manufacturers are researching various alternative raw ingredients different from traditional durum wheat due to rising demand for more healthy options amongst customers (pasta). One such example includes chickpea flour which provides a protein- rich gluten-free alternative meeting both health-conscious individuals’ demands as well as those suffering from gluten intolerance disorder. Another emerging ingredient is lentil flour not only does it provide more proteins but also gives pasta products unique flavors plus natural red colors (colors 280). Apart from quinoa they include teff, which are ancient grains that have high nutrient levels and distinct flavors hence satisfying special interest market which demands both dietetic benefits as well as fresh culinary exploration. By maintaining high quality in pasta manufacture, these alternatives allow for innovation and entry into niche consumer segments.
Innovations and Future Trends in Macaroni Production
Enhancing Efficiency through Automation
I am a pasta maker who has realized that automation in the production process really improves efficiency. Automation simplifies processes by reducing human effort and cutting down on errors that may occur from manual activities, resulting into uniform quality of products. The other aspect is that advanced machines and robots can facilitate large-scale production at faster rates for timely market demand fulfillment. Within this context, automation also allows better control and monitoring of such parameters as temperature, humidity which are vital to maintain the macaroni’s physical integrity. By doing so, I can make use of these technologies to optimize my resources reducing production costs hence making my offering superior to my consumer.
Consumer Driven Changes: New Shapes And Flavors
For example in macaroni business I have tried coming up with new shapes and flavors so as to meet the varying needs of consumers. Moreover, I still add lots of different forms like the radiatori or gemelli which bring about special pleasing appearances and feels inspired by the latest culinary trends and innovative recipes. Moreover I made sure there were various flavors for health conscious people including spinach, beetroot or turmeric among others who wanted exciting culinary experiences as well. And keeping pace with changes in tastes across all parts of market resulted in perfecting my product lines through constant updating while considering critics from top food websites.
Eco-friendly Aspects of Macaroni Production Techniques
To live up to my sustainability commitment, I have introduced several eco-friendly practices within the process of producing macaroni using such systems. My first step is making organic ingredients available locally in order to reduce carbon footprints related with transportation as they support sustainable farming practices through sourcing non-GMO ingredients from local suppliers Secondly investing in energy saving machines has helped me reduce carbon footprint by adopting green power sources like solar energy as well within my manufacturing plants. Thirdly water recycling systems have been installed instead for this valuable resource thereby ensuring effective usage until last droplet. Packaging has also seen tremendous changes to the extent that I now use biodegradable and recyclable materials. In a bit to save my environment pristine, I have embraced green approaches which have maintained my macaroni products’ high quality.
Reference sources
-
Loyal Pasta Machine: Unraveling the Production Macaroni Manufacturing Process
- This blog post from Loyal Pasta Machine offers an in-depth look at the entire macaroni production process, starting from the use of durum wheat semolina to the final stages of extrusion and packaging. It provides detailed insights into each step, making it a valuable resource for understanding how macaroni is made.
-
Barilla: How It’s Made – Pasta’s Journey from Farm to Table
- Barilla’s informative video delves into the journey of pasta production, explaining how durum wheat and water are transformed into high-quality pasta. This source covers critical stages such as milling, dough preparation, extrusion, and drying, providing a clear and comprehensive overview of the process.
- Watch Video
-
Made How: How Pasta is Made – Manufacture, Making, History
- The “Made How” website provides a thorough explanation of the pasta manufacturing process, including the historical context and modern practices. It details the stringent federal regulations and inspection routines that ensure the quality and safety of pasta products, offering a well-rounded perspective on the production process.
- Read More
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the initial steps in the process of macaroni manufacturing?
A: The initial steps for making macaroni require mixing water and farina to form dough that is then kneaded before it can be extruded through dies into any shape desired.
Q: How is dry pasta like macaroni made differently from fresh pasta?
A: Dry pasta, including various types of macaroni, undergoes a longer drying process at lower temperatures compared to fresh. This leads to a significant reduction in moisture content such that they can be stored for longer periods. In fresh pasta production, egg is often an additional ingredient, but dry pasta typically consists of only semolina and water.
Q: What types of manufacturing equipment are essential for a macaroni manufacturing business?
A: Vital machines used when producing macaroni include mixers used in preparing the dough ,extruders used in shaping the dough into different forms which results in macaroni ,drying tunnels or racks used in reducing moisture content as well as packaging machinery that prepares these products for selling.
Q: Can you explain the spaghetti process in comparison to macaroni manufacturing?
A: The spaghetti process is quite similar to that of making macaronis because it involves mixing semolina with water to form dough followed by extrusion. However there is difference between them with regards to how they are shaped after being extruded; spaghetti is usually extruded through a circular die into long thin strands while on the other hand Macaronis tubular shapes are produced by paste passed through die opening.
Q: What are some potential business opportunities in the macaroni manufacturing industry as of 2024?
A: By 2024 some business opportunities might involve developing organic and gluten free pastas, creating innovative flavors or ingredients and producing ready-to-cook dishes targeting fast-healthy food consumers who want quick meals that can be prepared without much fuss.
Q. What considerations go into developing a business plan for a macaroni manufacturing business?
A: For those looking to come up with a business plan for macaroni making, they will need to conduct market research in order to know the current demand, stipulate the products range, describe production process, specify types of machinery that are needed in manufacturing process, identify suppliers of materials such as semolina and water, prepare financial forecasts showing profitability and reasonableness of venture.