Many foods are loved by people worldwide, but pasta occupies a unique position in culinary art. This article looks into the intricacies of an automatic complete line used in pasta production, taking you through this fantastic journey, starting from fresh pasta to a well-dried product ready for consumption. The authors also seek to discuss the processes involved in its manufacture and how these systems help maintain the quality and taste that pasta lovers enjoy. It is anticipated that readers will better understand the science and art employed alongside innovation that can make something so familiar become a favorite meal.
What is a Pasta Production Line, and How Does it Work?

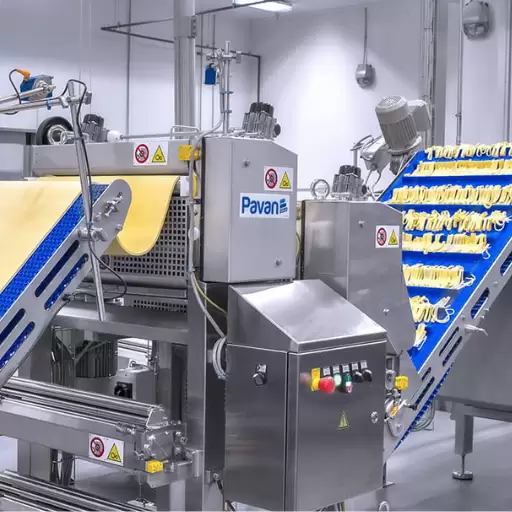
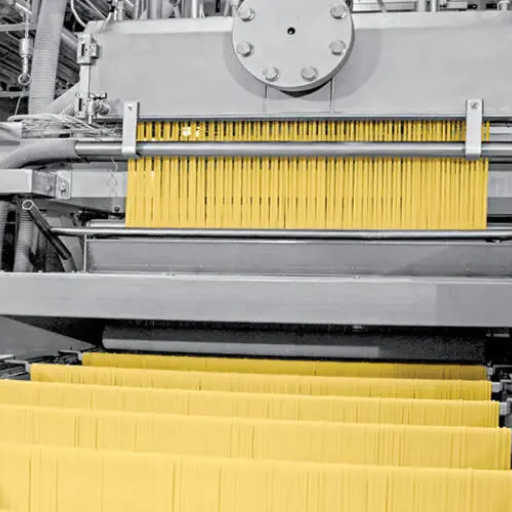
Image source: https://www.directindustry.com/
A comprehensive system designed to make pasta automatically from raw materials up to an end product, which is dry, comprises a pasta production line. This consists generally of several interconnected machines with various functions, such as mixing flour and water, shaping the dough, cutting it into specific shapes, and drying it. The process starts with weighing and mixing ingredients precisely, followed by kneading to form a homogeneous dough. Afterward, extrusion occurs, where the dough is forced through an extruder unit to be shaped into different forms of pasta. Finally, controlled environments are used in drying where appropriate texture for eating is reached while achieving shelf stability. Such automation makes them more efficient and ensures consistency and high standards for pasta products.
Overview of Pasta Production Line
To streamline the entire process of making pasta, the pasta production line is an integrated system that uses advanced technology to maximize efficiency and quality. Various industry experts, including market leaders and culinary websites, suggest that good quality durum wheat flour must be mixed with water first, creating a consistent dough. The stages include mixing, kneading, and dough sheeting, followed by cutting or extrusion processes that result in various pasta shapes. Such pasta is later dried under controlled conditions to reduce moisture content, increase shelf life, and improve texture. Automation has sped up each phase in modern pasta production lines and increased quality control to ensure that products meet consumer expectations worldwide. This efficiency also enhances precision, promoting scalability in pasta production to keep pace with the growing global demand for this essential food item.
Key Components Involved in Pasta Production
- Durum wheat flour: This is the main ingredient in making pasta; it has a high content of protein and gluten, which gives pasta structure and firmness. The taste and texture of the final product are directly affected by the quality of the flour.
- Water: To establish dough, it is essential as it hydrates flour, thus activating gluten formation, which helps to make dough manageable. The consistency of the paste depends on the amount of water added and the amount of flour used.
- Mixers and Kneading Equipment: These machines play a crucial role in mixing flour with water uniformly to develop gluten in the dough. Homogeneous mixing gives a consistent dough that is essential for uniformity in cooking and texture.
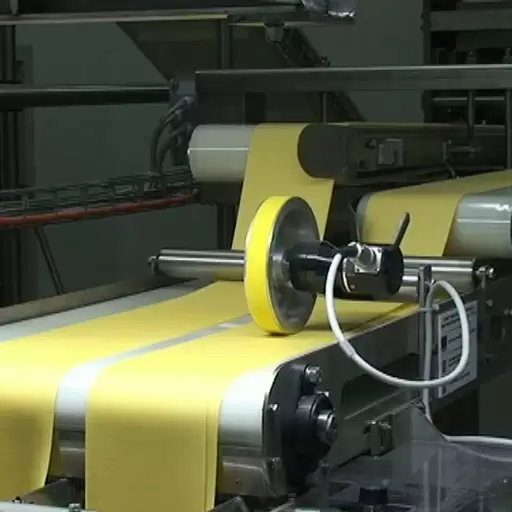
- Extruders and Cutters: These parts transform pasta into different shapes, such as long strands like spaghetti or hollow tubes like penne. A die presses dough through extruders while cutters chop it to appropriate sizes.
- Drying Systems: The drying process must be done correctly not to degrade quality and extend shelf life. Managed dehydration removes moisture while maintaining pasta’s structural integrity, preventing decay.
- Quality Control Systems: This ensures that all ingredients, from raw materials to finished products, comply with industry standards for processing safe consumer products.
These components form part of an up-to-date pasta manufacturing line that enhances effective production systems to address a broad market base with diverse tastes.
From Flour to Pasta: The Production Process
Pasta production involves many vital steps that transform these essential ingredients into the loved household food. First, a good semolina flour is selected as it is essential to achieve the right texture. The flour is then mixed with enough water to form a dough. The dough-kneading process helps develop the gluten to attain elasticity once kneaded. After kneading, the dough gets shaped using extruders or cutters depending on the desired pasta shape. Then, controlled drying systems remove moisture from pasta after shaping and protect its quality from spoilage. Lastly, quality control checks guarantee that health standards are met before packaging for distribution. A careful process ensures that this dish remains a predictable and mouthwatering favorite among millions.
How to Choose the Right Automatic Pasta Production Line?

Selecting an automatic line to produce pasta requires several things to consider. First, identify your company’s production capacity requirement based on business needs; therefore, look at your expected output rate. Consider searching for a line to manage your targeted production volumes without compromising its quality. Next, consider different shapes and sizes you may want to make within your equipment because not every machine can handle all types of pasta. Additionally, assess technology used in the pipeline regarding automation and energy consumption efficiency, which lower costs. It is also essential to review the manufacturing company’s reputation and maintenance services or training support availability. Lastly, lack of finance should be weighed against initial investment vis-à-vis long-term savings and increased productivity.
Factors to Consider: Production Capacity
When determining the production capacity for an automatic machine to produce pasta, you need to consider the following;
- Demand Forecasting: This is about analyzing consumer demand and market trends to predict how much pasta needs to be produced. In this way, choosing a line that can expand or contract with market changes becomes possible.
- Output Specifications: Look at the kilograms per hour or tons per day various lines can produce. Consequently, go for a line that meets your present requirements and has room for expansion.
- Shift Flexibility: You should evaluate if the production line can work effectively across several shifts. Equipment made for uninterrupted operations may have a significant impact on total productivity.
- Batch Size: Whether your production will mainly involve large runs or smaller assorted ones influences the selection of machinery based on flexibility or volume.
A thorough assessment of these factors will ensure that you choose an automated line for making spaghetti and other types of pasta that suit your business objectives and market trends.
Types of Fresh Pasta and Their Production Needs
To understand the various types of pasta for fresh pasta and their specific production needs, one must first be familiar with the different forms of pasta available and the corresponding machinery that is applicable to produce them.
- Tagliatelle: Its dough should be rolled into machines that can achieve a certain thickness before being cut into pieces. This means that cutter assembly lines need a variety of sizes.
- Ravioli: These require a seal that will protect the pasta and ensure even distribution of the fillings. The bulk production process often involves semiautomatic steps to maintain quality and speed.
- Fettuccine: It is also flat but usually wider than tagliatelle. This requires equipment that allows thicker doughs and more significant quantities to be processed simultaneously. One can only imagine the importance of a robust cutting tool and a drying system to avoid creating brittle or cracked fettuccine.
This understanding will enable businesses producing pasta to select appropriate equipment and processes to enhance their pasta production line’s efficiency and product quality.
Understanding Spaghetti and Short-cut Pasta Lines
Due to their shapes and ways of preparation, spaghetti or other short-cut shaped pasta needs special considerations compared to different types of pasta. For instance, long-sized thin spaghetti does not just mix doughs using kneading apparatuses but also continuously extrudes them into homogenized strands. A single screw extruder may be used during this operation since it accurately controls the size as well as the texture of this delicacy. Conversely, short-cut pasta such as penne or fusilli necessitates more flexible exudation methods to create diverse shapes quickly.
The drying stage is equally essential for both types; however, shorter sizes take longer due to their thickness and density. Short cuts require more extensive drying times than long cuts because their thickness makes them retain moisture for extended periods. Consequently, spaghetti and short-cut pasta manufacturers must tailor methods to suit food trends, optimize operations, and meet customer requirements as they change with time.
What are the Benefits of Using an Automatic Pasta Production Line?

There are many advantages to having an automatic pasta production line, and it can significantly enhance efficiency as well as the quality of the final product. Foremost, automation refines the whole process by reducing manual labor and minimizing human error, giving rise to consistent results. Secondly, these systems can work all day long, maximizing production capacity and ensuring that companies do not experience delays associated with manual tasks when meeting demands. Moreover, in most cases, automatic lines are equipped with high-tech gadgets that aid in the precise control of blending, kneading, and extrusion, thus producing top-quality pasta with a uniform texture. Lastly, adjusting quickly to various pasta shapes and recipes adds versatility to this technology, making it possible for producers to react promptly to altering customer preferences.
Increased Efficiency and Production Capability
There are many reasons for increased efficiency and output potential for automated pasta production lines. Firstly, these lines usually have modern machinery that optimizes every production stage, from ingredient blending to final packaging, hence minimal downtime. Reports published by websites such as Food and Beverage Industry News suggest that a company can see an up to 30% rise in its outputs after implementing automatic systems. Besides, IHS Markit shows that automation may significantly reduce wasted ingredients, with some factories reporting a reduction of up to 20%. Lastly, the Journal of Food Engineering claims that computerized lines have assumed real-time monitoring and adjustments, facilitating faster production rates and ensuring product consistency, thereby dealing with quality assurance and scalability issues.
Consistency in Pasta Quality
Pasta manufacturers who want to meet customers’ expectations and stick to industry laws must maintain consistency in pasta quality. Automated production lines control every stage of pasta manufacturing, from ingredient ratios to cooking times. The latter reports that automation guarantees that every batch of pasta is produced under the same conditions, minimizing differences in texture and aroma. Moreover, inline quality control systems are among other technologies used for continuously monitoring product attributes to make immediate adjustments to preserve uniformity in output. Hence, firms can deliver pasta products that meet and surpass market standards, thus fostering brand loyalty and trust.
Reduced Labor and Operational Costs
Automation has drastically reduced labor and operational costs associated with pasta making. Industry research findings indicate that such automated systems require fewer personnel supervising the process, hence enabling businesses to allocate human capital more optimally. According to McKinsey and Company, businesses can cut labor costs by 20% while raising overall efficiency (McKinsey and Company). In addition, Forbes highlights an aspect such as automation that makes it possible for people not to make mistakes, thereby cutting down on recall efforts and reducing the reworking involved with defective merchandise. Lastly, Deloitte surveyed processes indicating optimized resource management due to shorter production cycles, which allows streamlining operations and swift response without added labor cost (Deloitte). These reduced workforce requirements and better process efficiency positions mean substantial savings over time for manufacturers. However, higher operational effectiveness channels can be achieved within one company’s domain.
What are the Differences Between Fresh and Dry Pasta Lines?

The ingredients used to make fresh and dried pasta significantly differ; similarly, the way they are manufactured varies, as does storage. Fresh pasta is frequently prepared with eggs and flour. Thus, it has a softer texture and a shorter shelf life that requires keeping it in a refrigerator and using it within a few days of its production. On the other hand, dry pasta is made from semolina flour and water, followed by long drying periods to reduce its moisture content; hence, it can be stored longer at average temperatures. Because of this different storage approach, dry pasta is always preferred in the food industry. Furthermore, while fresh pasta takes less time to cook, dry pasta takes more time, affecting commercial kitchens’ preparation techniques. Also, when preparing different dishes, these two pasta types bring different flavors or textures depending on how you like them.
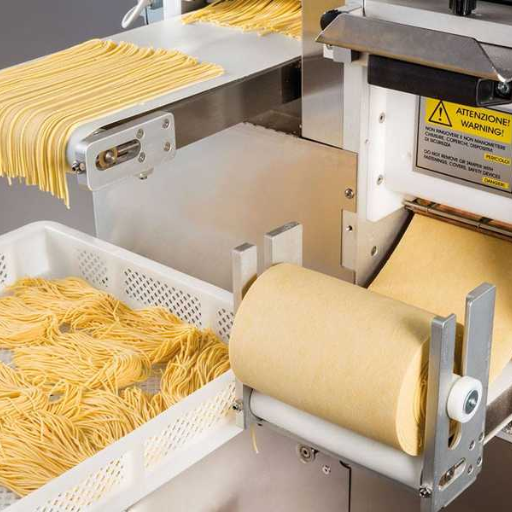
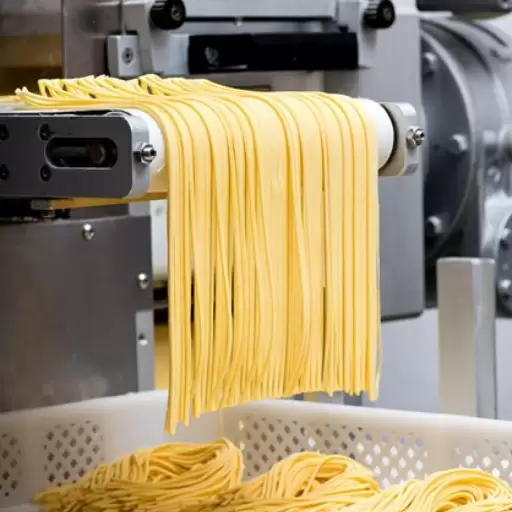
Manufacturing Processes for Fresh Pasta
Fresh pasta is made by mixing quality eggs and flour to make dough, which is then rolled. First, the ingredients—maybe water—are blended in particular proportions to get the intended consistency and texture. Subsequently, sufficient kneading encourages gluten formation to enhance the elasticity of this paste. The gluten needs some time off after it’s been well worked.
The rested dough will be passed through a pasta sheeter that rolls it to the required thickness. Thereafter, the rolled dough will be cut into lasagna sheets, fettuccine, or ravioli as appropriate for use. For direct cooking or dusting with flour and packaging. Refrigeration should follow immediately after the production of fresh pasta to save on its high value and prevent spoilage because it has a limited shelf life compared with dried pasta.
Though automation may help some manufacturers make these processes straightforward, attention to detail regarding ingredient quality and production methods remains essential for real fresh pasta.
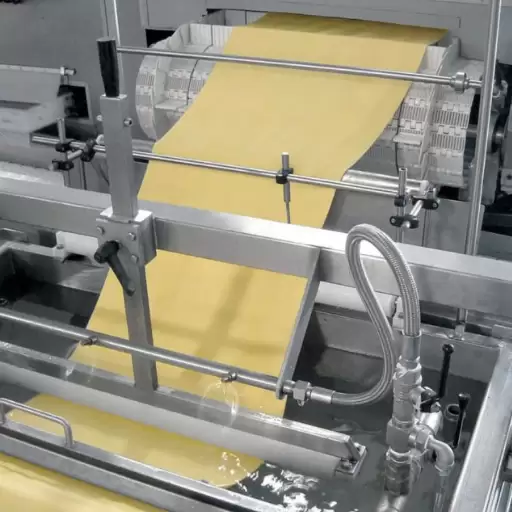
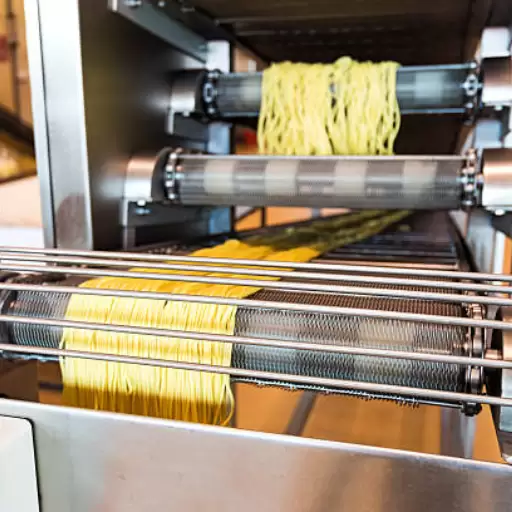
The Drying Process for Long-cut and Short-cut Pasta
The drying process is critical in achieving the right texture and extending the shelf life for both long-cut and short-cut pasta. Whether spaghetti, penne, or rigatoni, once the pasta has been shaped, it goes through a drying process, often involving controlled temperature and humidity levels. This step draws the moisture content away without destroying its cohesion.
Drying time for long-cut pasta like spaghetti can range from 12-24 hours as they need even drying of the thin strands to prevent them from clumping together. Short-cut pasta, on the other hand, dries more quickly because of its smaller size and surface area. Manufacturers employ methods such as hot air drying to maintain the natural color and flavor while ensuring uniform moisture removal. To ensure it reaches consumers in good condition. It is ready for use, and the last product should be put in moisture-proof materials during packaging to maintain its quality while stored or transported.
Storage and Packaging Considerations
Pasta should be stored appropriately and packaged to maintain its freshness and quality. Fresh pasta must be kept in a refrigerator at 39°F (4°C) below, lasting 2-3 days. It is best when wrapped or contained in an airtight container that keeps it moist. Freezing fresh pasta allows it to last longer, up to several months, but it must be put in either freezer-safe containers or vacuum-sealed packages to prevent freezer burn.
In contrast, dried pasta can be preserved for long periods and stored in a cool place devoid of moisture, preferably inside its original package or a fitting air-tight container. Proper packaging with materials that do not allow moisture is essential because if not done so, humidity will dampen the product, thus promoting invasion by pests. If kept properly, dried pasta may go on for several years, but within 1-2 years, this is recommended for best quality consumption. For both types of pasta, sunlight should be avoided as much as possible while storing them at places with constant temperatures to ensure the highest culinary results possible.
How do you maintain and troubleshoot pasta production machinery?

Pasta-making machines require constant examination, washing, and prompt fixing to maximize productivity. The first step is to observe the maintenance schedule provided by the manufacturer, which generally includes greasing movable parts, tightening bolts, and inspecting belts for tear and wear. Each day, the cleaning measures involve clearing any dough remains or flour dust that can contaminate the materials.
If there is a problem such as irregular shape or uneven drying process, look at obstructions within the machinery and check whether all its components function correctly. Calibration may be necessary where there are deviations from expectations regarding product dimensions or moisture levels. It is also good to keep track of machine temperatures during production and humidity levels since they help detect problems before it is too late. A detailed maintenance history helps troubleshoot issues efficiently as one can know what persists continuously and when it should be fixed next.
Routine Maintenance for Optimal Performance
To ensure that the pasta production machines are maintained at an optimal level, it is necessary to establish a regular maintenance program that focuses on critical areas. Regularly inspect and clean machines to remove debris and prevent accumulations that could interfere with operations. Reference the manufacturer’s instructions for appropriate maintenance activities like lubricating moving parts and checking alignment. Also, the electrical system and components should be checked to avoid breakdowns. For troubleshooting purposes, maintain a record of operational performance because it will help identify trends and solve issues faster. Lastly, train employees about proper equipment usage practices to reduce damage and prolong machine life, yielding uniform product quality.
Common Issues and Their Solutions
- Pasta’s Irregular Shaping: Among the many problems faced in pasta production, irregular shaping remains common. This is usually due to inconsistencies in dough making or machine setup. To deal with this, ensure the dough is mixed well enough and the machine settings are properly set for a particular pasta shape. Constantly confirming feed rates and making necessary adjustments may also help produce uniform products.
- Drying That Is Not Uniform: Inconsistent drying will lead to defects in the final product. It could be caused by changes in humidity inside the drying chamber or poor air movement. To address such shortcomings, pay close attention to environmental factors and modify your drying processes accordingly. Always ascertain that the drying system works properly and that optimal air circulation is within the chamber.
-
Machine Problems: Machine breakdowns like blockages or failure to work can significantly affect output. These issues can be prevented through regular cleaning and checking of machinery, which stops buildups of waste materials from leading to this occurrence. Therefore, a comprehensive maintenance program should be instituted alongside timely repairs as they will help prevent these occurrences from happening again. Whenever a machine breaks down, its troubleshooting guide should be referred to since it gives immediate answers, enhancing productivity once more.
What Innovations are Coming in the Pasta Production Industry?

Several changes are being made to improve efficiency and product quality in the pasta production industry. The use of intelligent technology, such as IoT-enabled machines, is one such improvement that enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This can result in a reduction in downtime and an increase in general productivity. In addition, eco-friendly packaging solutions and the emergence of alternative flours like those derived from legumes or ancient grains are becoming popular among health-conscious consumers and those with special diets. Automation has also been adopted in sorting and packaging processes to reduce human error during the production workflow, making it much more efficient.
Advancements in Pasta Maker and Extruder Technology
Recent advancements in pasta makers and extruders have improved the quality and efficiency of production processes. This has led to better control over extrusions, resulting in more uniform pasta shapes and sizes through precision engineering techniques used by leading manufacturers. Advanced materials used in machines increase durability while reducing wear.
The most modern pasta extruders have automated systems that can adjust pressure and temperature settings in real-time. This reduces energy consumption while ensuring optimal cooking properties. In addition, 3D printing technology for pasta production is also being explored by companies, which allows customized shapes and designs for personalized experiences among consumers. Such innovations respond to the rising demand for artisanal pasta products and promote scalability, thus meeting different market requirements during mass production.
Automation and Smart Manufacturing Solutions
The food production sector is being transformed by automation and intelligent manufacturing technologies, which deliver greater efficiency, lower costs, and better quality products. Leading manufacturers increasingly use the Internet of Things (IoT) to monitor and analyze data in real-time, which can be used to improve production processes based on immediate insights. Predictive maintenance is made possible through this connectivity, thereby reducing downtime and increasing the lifespan of machines. Moreover, machine learning algorithms are applied to examine production data for continuous quality control and resource management improvement. In addition, robotics play an essential role by automating repetitive tasks, thus reducing human error and enhancing worker safety. These developments not only make operations more efficient but also promote sustainability through waste minimization and reduced energy consumption during the manufacturing process.
The Future of Pasta Processing Lines
Pasta processing lines are expected to be highly impacted by technology. Companies now focus on automation and intelligent technologies for better production efficiency. Artificial intelligence that can forecast demand is among the key trends being adopted, and machine learning continuously optimizes processes. With energy-efficient equipment and eco-friendly packaging becoming widely used, sustainable practices have also gained traction in this field. Moreover, there has been a movement towards customization where pasta makers use flexible production lines to produce different shapes and sizes to meet consumer preferences. All in all, these innovations will help pasta manufacturers become more competitive in an ever-changing marketplace.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is an automatic complete pasta production line?
A: An automatic complete pasta production line is a system designed to efficiently produce various types of pasta, including fresh pasta, from start to finish. This system typically includes stages for mixing raw materials, extruding dough into pasta shapes, drying, and packing.
Q: How does a spaghetti production line differ from a macaroni pasta production line?
A: A spaghetti production line is designed explicitly for long-cut pasta, while a macaroni production line is optimized for short-cut pasta shapes like macaroni. Each line has specialized equipment to handle the unique production requirements of different pasta shapes.
Q: What types of pasta can be produced using a fresh pasta production line?
A: A fresh pasta production line can produce various types of pasta, including long-cut spaghetti and short-cut pasta, such as macaroni and shells. The specific shapes depend on the extruding equipment used in the line.
Q: What are the critical components of a pasta-making machine?
A: Key components of a pasta-making machine typically include a mixer for combining ingredients, a screw-based extruder for shaping the pasta, a dryer for removing moisture, and a packing machine for final packaging.
Q: Why is stainless steel often used in pasta production lines?
A: Stainless steel is favored in pasta production lines because of its durability, resistance to corrosion, and ease of cleaning. This ensures that the machinery remains hygienic and operates efficiently over time.
Q: Can a single screw extruder be used for both spaghetti and macaroni production?
A: Yes, a single screw extruder can often be adapted to produce both spaghetti and macaroni by using different dies and adjusting the machine’s settings to accommodate the specific requirements of each pasta type.
Q: What role does a vacuum system play in pasta production?
A: A vacuum system is crucial in the pasta production process. It helps remove air bubbles in the dough mixture, ensuring a smooth and uniform texture in the final pasta product. This is particularly important for high-quality pasta production.
Q: How can a facility optimize its pasta production capabilities?
A: Facilities can optimize pasta production capabilities by upgrading to an automatic complete pasta production line, using high-quality raw materials, and implementing advanced control systems like PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) for precise operation and monitoring.
Q: What is the production capacity of most industrial pasta production lines?
A: Industrial pasta production lines’ capacity can vary significantly, but they are generally designed to produce hundreds to thousands of kilograms per hour, depending on the specific system and its configuration.
Q: How do I choose a supplier for a pasta-making machine?
A: When choosing a supplier for a pasta-making machine, consider factors such as their experience in the industry, the quality of their equipment, customer reviews, and their ability to provide complete turnkey solutions. Ensure they can support your manufacturing capabilities and specific production needs.