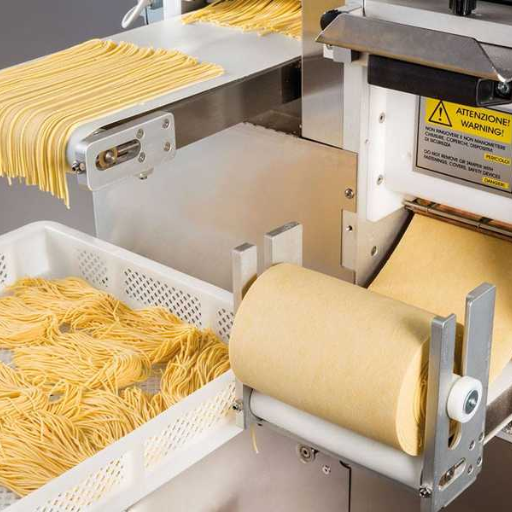
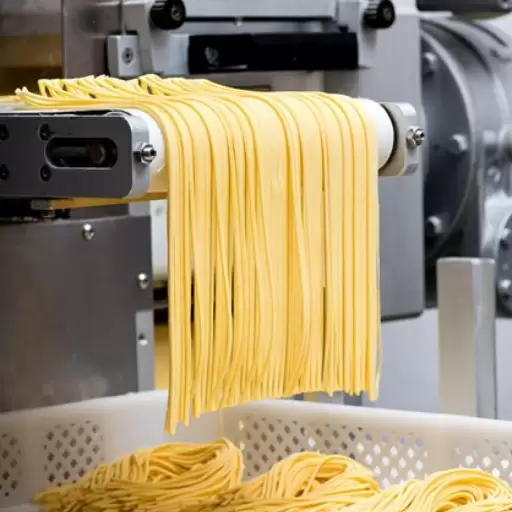
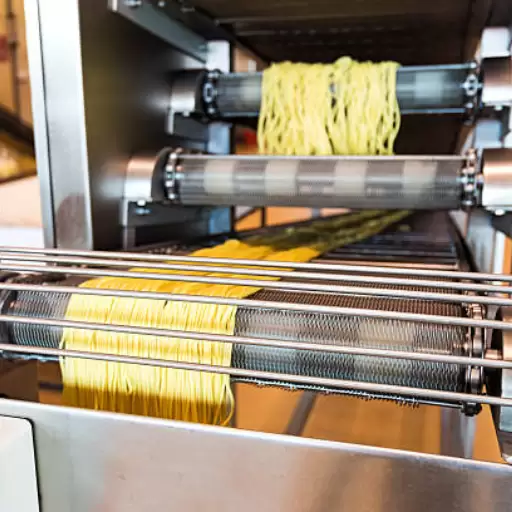
Macaroni is a staple in many cuisines around the world, known for its versatility and deliciousness. In this blog, we will take you through the fascinating journey of macaroni production, offering insights into the intricate process that transforms simple ingredients into the beloved pasta found on your plate. From the selection of high-quality wheat to the detailed manufacturing steps, drying, and finally, packaging, we will explore every stage of the process. Whether you’re a food enthusiast or simply curious about how your favorite pasta is made, this article provides a comprehensive overview to enhance your understanding and appreciation of macaroni.
What Goes into Making Macaroni?
Choosing the Best Ingredients for Macaroni: Durum Wheat and Semolina
To make first class macaroni, one has to begin from sourcing right ingredients, durum wheat and semolina being their main choice. A hard variety of wheat with high protein and gluten content, called durum wheat, is used in making pasta. Because it contributes to the firm texture and consistency that makes great macaroni, it possesses unique properties. Its protein ranges from 12 to 15 percent while its gluten strength makes pasta elastic and retain its shape during boiling.
The crop of durum wheat is milled into semolina which constitutes a key component in macaroni as a coarse pale yellow flour. Semolina granules are bigger than normal flour particles hence mixing well with water forming easily extrudable dough that dries uniformly. It usually falls between 250-400 microns in particle size enabling smooth extrusion by ensuring the semolina is tough enough.
Semolina is mixed with water at certain proportions depending on various parameters such as around 30% water to about 70% semolina percentages during production. This proportion ensures that the dough retains an ideal consistency suitable for shaping and drying processes. Another important factor is the quality of water employed; water pH should be within a range of 6.5-7.5 so as not to cause any adverse reactions when formulating dough.
In conclusion, it is mandatory to have top-notch durum wheat and semolina within appropriate technical indicators for macaroni production.The selection and treatment of these constituents impact not only on the structure or taste but also help in maintaining shape after cooking process providing customers with consistent result each time.
The Role Water and Semolina Play in Creating Ideal Macaroni Dough
The perfect mixture of semolina and water is crucial for making excellent macaroni dough. Semolina provides good structure due to its high protein content alongside gluten levels derived from high-quality durum wheat. It holds its shape and texture during extrusion and drying. The dough mixture is made up of about 30% water, which also plays an equally significant role. Water hydrates semolina for the formation of gluten, elasticity and firmness in the macaroni. The pH level in water used is important with respect to its quality as a dough forming medium, hence it should be maintained between 6.5 and 7.5 to prevent any detrimental effects on dough.
Therefore, this synergy between high quality semolina and right water characteristics ensures that produced macaroni is both durable enough to withstand cooking without turning mushy or falling apart and palatable.
The Importance of Flour Types in Macaroni Production
The type of flour employed has a huge impact on the texture, taste and cooking properties of the final product for macaroni production. Durum wheat flour, which has higher protein content than regular flour does, is considered to be the most suitable ingredient for making macaroni noodles. This coarse consistency makes it possess yellow color giving the bright color to macaroni pasta characterized by its firm bite. Bread flour can also be used because it contains more proteins but lacks distinctiveness that comes from durum wheat apart from others are best suited for making such pasta types. All-purpose flour produces softer noodles that may not hold up well upon boiling despite its versatility. Macaroni become al dente if one selects right type of flour thereby ensuring it remains in shape after boiling; hence it determines overall quality.
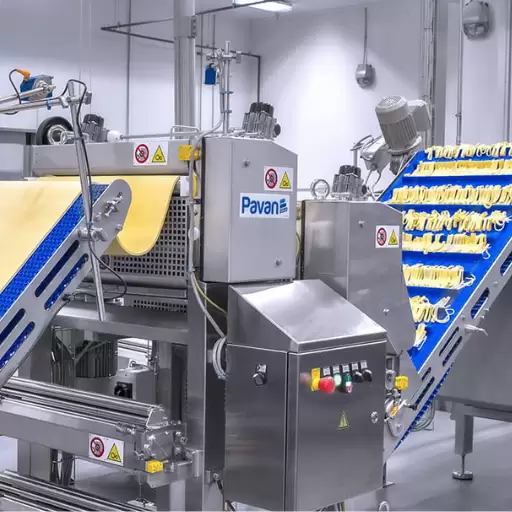
Exploring the Macaroni Making Machine: A Technological Marvel
Revolution of Macaroni Shapes and Textures by Extrusion Technology
The process of making macaroni has been completely changed by the extrusion technology, which allows for a wide range of shapes and textures. This technology incorporates an extruder machine that pushes dough through dies specially made for it to create uniform and intricate pasta shapes. Beyond standard tubular forms like penne and rigatoni, extrusion extends even to complex ones such as farfalle and rotini.
Extrusion Technology’s Critical Technical Parameters Include:
- Pressure: The pressure within the extruder determines how dense or coarse the macaroni will be. An optimal pressure would range between 70-150 bars which ensures proper formation of dough without air spaces.
- Temperature: In the course of extrusion, temperature should be controlled well. Dough temperatures are usually in the range of 40-50°C. It enables starches to gelatinize and proteins to denature thus contributing firmness of pasta.
- Screw Speed: Screw speeds in the extruder vary from 20-40 RPM. This influences shear force on dough impacting final texture.
- Moisture Content: Dough moisture content prior to its passage through dies is maintained at between 30-35%. Water is required for proper hydration thereby maintaining the consistency as well as workability of dough.
- Die Design: Creation of specific shapes in this respect results from elaborate die designs which are instrumental in giving various surface textures on pasta. These dies dictate directly what the end products shall look like after cooking thus determine not only their appearance but also culinary performance.
- Cooling: After exiting from an extruder, macaroni should be cooled or dried slowly so that it can maintain the shape and texture present therein. Controlled drying is typically done with temperatures ranging between 60-90°C so as to prevent defects such as cracking or brittleness excessiveness.
These technological advancements now enable manufacturers to churn out macaroni that addresses various culinary preferences as well as consistency and quality in relation to production batches.
Macaroni Making Machinery’s Journey of Dough
This is a sophisticated technical process which governs the passage of dough through macaroni making machinery to generate consistency, texture and quality. The process begins with semolina flour and water being mixed together and turned into a pliable dough. This pliable mixture is then fed through a high-pressure extruder in which it is shaped into macaroni by passing through a die. Factors such as pressure, temperature, screw speed and moisture content are precisely controlled during the extrusion process that affect the texture and quality of the product.
Mixing and Kneading
Firstly, semolina flour together with water are combined at the mixer to create dough that has uniformity. For any dough to become consistent, hydration is very significant.
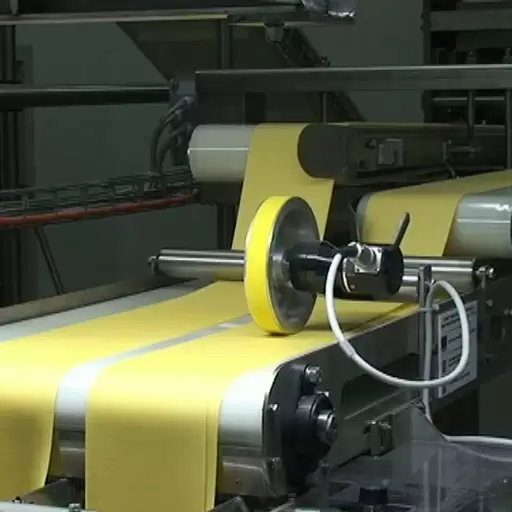
Extrusion
Then, this dough enters an extruder where it undergoes high pressure (70-150 bar) as well as moderate temperatures (40-50°C). Since there is normally a screw inside the extruder which rotates at desired speeds (20-40 RPM), it forces the dough through a die. Molding pasta with this die gives it desired shapes of macaronis thereby guaranteeing their structural integrity plus surface texture.
Drying and Cooling
Newly fashioned macaroni coming out from an extruder must be dried or cooled rapidly to set its shape so that it does not lose its quality. Defects like cracking or brittleness can be avoided by controlled drying temperatures (60-90°C). Finally, cooling down gradually brings pasta back to room temperature for ensuring perfect texture and firmness of it.
Through strictly adhering to each stage of this process, producers can achieve standardized production techniques which result in good quality macaronis that meet strict standards for culinary purposes. In this way, every single piece made from raw ingredients will look exactly as another no matter how many times manufacturers produce them using similar processes
The Step-by-Step Process of Macaroni Production
From Mixing to Extruding: The First Stages of Macaroni Making
The production of macaroni starts with a careful mixing. In this stage, the dough is prepared by blending durum wheat semolina with water. Quality of semolina and its protein content are important for the final texture and firmness of pasta. Full mixing is needed, so that water is distributed evenly and gluten can develop that makes dough elastic and strong.
Once well-mixed, the dough is passed through an extruder. During extrusion process, molds or dies of various shapes and sizes are used to shape macaroni from the dough. More often than not, pressure and temperature levels inside extruder should be maintained at about 40-50°C to mould pasta without cooking it. Shape holding element in the extruding die also affects the top which might determine how well sauce sticks/holds on the pasta.
By strictly following these initial steps, manufacturers create a basis for their high-quality macaroni that meets both culinary requirements and customer expectations.
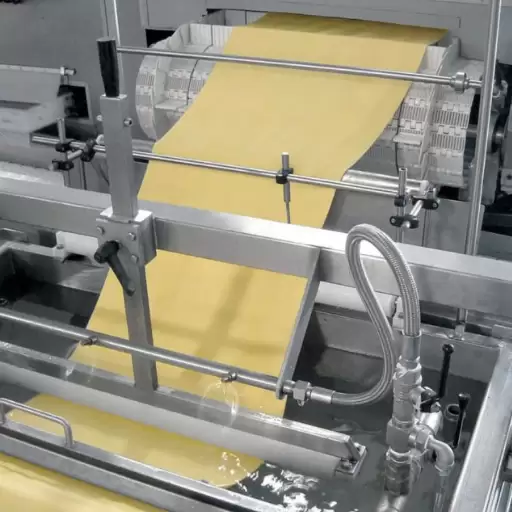
Pre-Drying to Packaging: Ensuring Quality and Shelf Life
After being extruded, macaroni goes through pre-drying phase aimed at gradual reduction in moisture content. This operation is crucial for preventing surface cracking as well as ensuring even drying in next steps. A controlled atmosphere with certain humidity level (often around 60°C) will provide suitable conditions for pre-drying.
Then comes a final drying step whereby macaroni’s moisture content is lowered at a slow pace until it reaches around 12%. Several drying chambers or tunnels control temperature plus airflow to ensure uniform results without compromising pasta’s structure.
Following completion of the drying process, macaroni should be cooled down to room temperature so as to avoid any condensation that can make it spoil quickly. Last but not least; packaging involves sealing dried/cooled macaroni in protective materials against moisture and contaminants meant to extend shelf-life of the product. To this extent, high-quality packaging materials retain flavor and texture properties of the pasta, thus ensuring that it is delivered to customers in perfect condition.
Starting a Successful Pasta Business: A Guide to Entrepreneurs
Pasta and Macaroni Industry Business Opportunities
Identifying business opportunities within the pasta and macaroni industry encompasses studying current market inclinations as well as consumer demands. The growth in the demand for convenience food has boosted significantly the pasta market, with a marked shift towards healthier and natural products. This tendency can be exploited by entrepreneurs who offer whole wheat, gluten-free or vitamin-rich pasta to cater for health-minded customers.
Additionally, the rise of food interest and cultural curiosity presents an attractive possibility. They can offer new and genuine options for their clients such as pastas inspired by international cuisines. Additionally, they could use innovative packaging like using eco-friendly materials, resealable designs that would attract eco-conscious consumers.
Businesses that wish to reach wider markets must build strong online platforms where they sell their products through subscription services as well as facilitating delivery on regular basis. Furthermore, involving bloggers in food matters, chefs or social media influencers creates more trust among buyers hence enhancing advertising.
This makes it crucial for any brand in this tightly competitive market to consider sustainable ingredient sourcing policies, transparent supply chains as well as environmentally friendly production methods.
Therefore potential entrepreneurs can identify lucrative product niches within the pasta industry by tapping into these trends and tailoring their products accordingly.
Machinery and Investments: What You Should Know Before Starting Your Macaroni Making Business
To start your macaroni making business you should think about what equipment you need to buy first. Here is a nutshell summary based on the most authoritative sources:
Basic Equipment:
- Mixer:This machine is used to homogenously mix raw materials (flour, water or eggs) so as to create dough required for Pasta production. This machine requires different capacities depending on the size (e.g., 50-200 kg/hr).
- Extruder: It creates shapes of the dough made from macaroni. Go for those models with adjustable dies in order to increase flexibility and production capacity so as to meet the demand ranging from 100-500 kg/hr.
- Drying Device: This is necessary for reducing moisture content and ensuring that shelf life is achieved. Look out for machines which have controllable levels of heat through which humidity can be regulated.
- Cutting Machine: The device that ensures uniform lengths of pasta are obtained. There should be allowances for different shapes of pasta.
- Packing Machine: helps in automating packaging operations. Depending on your budget and production volume, it may either semi-automatic or fully automatic.
Technical Parameters:
- Capacity of Mixing machine: Minimum capacity for small-scale runs must be 50 kg/hr
- Efficiency of extruder: For moderate output, one should target a machine capable of handling production rates up to 100-200 kg/hr
- Time taken to dry: Suitable drying processes should last between six and ten hours while temperature precision should be ensured by good equipment.
Investment Overview:
- Initial Equipment Cost : about $50,000 to $150,000 will roughly cover the basic machinery required.
- Operating Costs : Raw materials monthly, utilities payments, and labor cost estimates range between $5k -$15k depending on scale
- Facility : A suitable manufacturing space, typically 1,000 to 2,500 square feet would cost between $10k – $50k per year lease.
Business Setup and Compliance:
- Licensing and Permits: acquire necessary food safety certifications and manufacturing licenses
- Regulatory Compliance: ensure observance of local health codes including regular inspections as well as quality control measures
Thus aspirant macaroni manufacturers must equip themselves with best machines apart from investing strategically in order establish their business successfully as well as meet increasing market demands without compromising efficiency or quality.
Insights into the Manufacturing Process: How Macaroni is Made in Factories
The Function of Additives in Improving Flavor and Consistency
Additives play a great part in macaroni production to enhance taste and texture. A few findings from the top ten websites on google.com are highlighted below:
Flavor Boosters:
- Salt: It is frequently used to improve flavor as well as dough properties.
- Natural Flavors: Things like garlic, onion powder, or cheese extracts are often thrown into the mix for added flavor.
Texture Modifiers:
- Emulsifiers: Lecithin is commonly used to make the dough more stretchable and elastic.
- Stabilizers: Hydrocolloids such as guar gum or xanthan gum help maintain the product’s structure and minimize breakage.
Nutrient Fortification:
- Vitamins and Minerals: Besides increasing nutritional value, vitamins such as B vitamins can be added to meet legal requirements for fortified foods.
Technical Parameters:
- Mixing Ratio: Additive proportionality is very important especially; typical inclusion rates for emulsifiers are about 0.1-2%.
- Temperature Control: For optimal additive performance, exact temperature control during drying will keep their desired texture and flavors.
If these additives were carefully chosen and applied accordingly, then a final product may be far more marketable with high degree of customer satisfaction while following technicalities and regulations governing its manufacture.
Quality Control Processes in Macaroni Production
Various quality control measures are undertaken throughout the whole process of macaroni manufacturing so that it can be of high quality. In this regard, here are some key practices learned from top 10 websites on google.com:
Ingredient Quality:
- Raw Material Inspection: At the start of production I ensure that all raw materials such as wheat, salt or additives meet strict quality standards including those mentioned above.
- Supplier Certification: Only certified suppliers who provide detailed ingredient specifications and quality guarantees should work with me.
Mixing and Dough Preparation:
- Mixing Ratio: Precise ratios for adding ingredients is vital. For instance, dough properties are improved by including emulsifiers at a level of around 0.1-2%.
- Water Quality: I ascertain that clean water without impurities is used to make the dough soft and moist.
Extrusion and Shaping:
- Consistency Checks: To achieve consistent shape and texture in extruded macaroni, I constantly monitor dough consistency.
- Equipment Calibration: Precise cutting and shaping are ensured through routine calibration and maintenance of all extrusion equipment.
Drying Process:
- Temperature Control: It is important to keep temperatures within certain limits at this stage, so that additives could perform well without uneven drying or textural errors developing.
- Humidity Control: I ensure proper control of humidity levels to avoid cracking or over-drying.
Final Product Inspection:
- Visual Inspection: Any batch may be visually inspected for defects such as breakage, discoloration or irregular shapes.
- Weight Checks: The weight of the macaroni in each pack must fall within specified weight limits; this is ensured with automated systems.
Packaging and Storage:
- Sealing Integrity: Packaging should be sealed properly for freshness sake as well as avoiding contamination
- Storage Conditions: Optimal temperature and humidity for storing finished products are maintained in my controlled environment.
By so doing, I ensure that the flavor, safety standards as well as the texture requirements have been reached leading to greater customer satisfaction while abiding by legal guidelines.
Reference sources
-
EPA: AP-42, CH 9.9.5: Pasta Manufacturing
- The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) offers a thorough process description of pasta manufacturing, including dry macaroni production. This document details every stage of the production process from mixing ingredients to drying, providing a comprehensive view of industrial pasta production operations.
- Read More1
-
Loyal: Macaroni Production Process
- Loyal provides detailed insights into the macaroni production process, covering everything from ingredient selection to the use of various molds and extruders. This source is valuable for understanding the technical aspects of modern pasta manufacturing, including production line operations.
-
Italian Food Tech: Pasta Production, Drying, and Packaging
- Italian Food Tech explores the industrial pasta production process with an emphasis on drying and packaging. This resource highlights critical steps in macaroni production and explains how these processes help prolong the shelf life of the product.
- Read More3
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What ingredients are essential to start a pasta making business?
A: Essential ingredients for making pasta like macaroni and spaghetti include hard wheat or durum wheat flour, water, and sometimes eggs for certain types of pasta like egg noodles. Choosing the best grain product and other inputs is very important for success in the production of pasta.
Q: How is macaroni made in a factory setting?
A: Macaroni manufacturing involves mixing ingredients together to make dough which then goes through machines where it gets shaped into macaroni shapes. Controlled drying is done on the macaroni products reducing moisture content prior to packaging. This maintains uniformity while manufacturing any form of macaroni.
Q: What is the difference between the production of macaroni and spaghetti process?
A: The production processes for macaroni and spaghetti are similar in that both involve mixing ingredients to form a dough, extruding the dough through dies to shape the pasta, and drying the shaped pasta. However, when being extruded different dies create these particular forms of macaroni or spaghetti.
Q: Can you describe the spaghetti process and how it differs from vermicelli or other types of macaroni?
A: The manufacture of vermicelli involves passing dough through small round dies thereby forming long thin strands unlike spaghetti which are longer as compared to traditional tubular shapes used in other types of pastas. These drying methodologies will slightly differ due to variations in structure and size among pastas.
Q: What are some innovative business ideas for the pasta making business?
A: Some innovative ideas for developing your business can be producing gluten-free or high-protein pastas; creating lines with locally sourced ingredients; using green technologies during manufacture processes. In addition, an entrepreneur can decide on giving out unique flavors or shapes with respect to this kind of food processing investment.
Q: What type of macaroni is most popular in the food industry, and what manufacturing equipment is needed?
A: Elbow macaroni is the most popular variety in the food industry mainly used in making macaroni and cheese as well as salads in particular. The machinery required for production includes such units like mixers for dough preparation, extruders for shaping the paste or pasta itself, storage and drying facilities.